Eyebrow hair loss, or madarosis, is a condition that Can impact people of all genders, often leading to self-esteem issues due to changes in appearance. But some hair thinning is natural, significant eyebrow loss can be concerning.
The condition typically affects adults aged 20 to 40, but it can occur at any age, with older individuals, especially for those undergoing hormonal changes like menopause, being more at high risk.
Women may face it more frequently than men, largely due to factors like cosmetic over-plucking and hormonal fluctuations. In India, around 20-25% of the population experiences it yearly, with lifestyle factors, health issues, and also taking so much of stress contributing to the rise.
What is Eyebrow Hair Loss?
Eyebrow Thinning: What It Really Means
It is also known medically as madarosis, which refers to the thinning or complete loss of your eyebrow hairs. Eyebrows play a crucial role in facial expression, your appearance, and losing eyebrows can noticeably change your appearance. It’s normal for some hair to fall out occasionally, but if it happens excessively or for a long time, it can be a matter of concern.
In terms of appearance, the individual may notice thinning in the brow region or patches where the hair has completely disappeared, which can signify an underlying health concern.
What Are the Types of Madarosis?
Understanding the Types of Madarosis
Madarosis can occur due to various factors, broadly classified into primary, secondary, and stress-induced types. Each type has distinct causes, ranging from genetic predisposition to underlying health conditions and stress-related factors.
– Primary Madarosis (Genetic Causes)
Primary madarosis refers to eyebrow loss caused by genetic factors or hereditary conditions. Individuals with a family history of hair thinning or loss are more likely to experience this type of madarosis.
Since genetics influence hair growth patterns, some people may have naturally sparse or thinning eyebrows from an early age. Unlike other forms of hair loss, genetic madarosis is often permanent and does not respond well to conventional regrowth treatments.
- Eyebrow Hypotrichosis – Hypotrichosis is a genetic condition that may cause thin or underdeveloped eyebrows from your birth.
- Non-Regenerative Hair Loss – Unlike temporary eyebrow thinning, genetic madarosis typically does not reverse on its own, making treatments like eyebrow transplants or microblading necessary for restoration.
- Androgenetic Alopecia – Commonly known as male or female pattern baldness, it primarily affects the scalp but can also lead to gradual eyebrow thinning, especially in senior citizens.
– Secondary Madarosis (Health Conditions Contributing to Hair Loss)
Secondary madarosis occurs due to underlying health conditions, medical treatments, or lifestyle factors. Unlike genetic eyebrow loss, this type is often reversible if the root cause is addressed in time. Health conditions, hormonal imbalances, and nutritional deficiencies are some of the leading contributors.
- Autoimmune Diseases – Conditions like alopecia areata attack hair follicles, leading to sudden eyebrow thinning or complete loss.
- Thyroid Disorders – Hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can disrupt the hair growth cycle, causing gradual eyebrow thinning.
- PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome) – Hormonal imbalances in women can contribute to eyebrow hair loss along with scalp thinning.
- Vitamin and Nutrient Deficiencies – A lack of biotin, iron (anemia), or essential vitamins weakens hair follicles, leading to excessive shedding.
- Chronic Inflammation – Skin conditions like seborrheic dermatitis or eczema can cause irritation and contribute to eyebrow hair loss.
– Stress-Induced Madarosis (Effects of Stress on it)
Stress-induced madarosis happens when emotional or psychological stress forces hair follicles into a resting phase known as telogen effluvium, leading to excessive shedding.
Hair loss is commonly delayed, appearing weeks or months after a stressful event. While temporary, prolonged stress can lead to continued eyebrow thinning if it’s not addressed.
- Triggers –Madarosis triggered by Work pressure, personal problems, trauma, anxiety, or sudden lifestyle changes can all contribute.
- Hormonal Impact –High levels of cortisol, a stress hormone, disrupt the natural hair growth cycle. People of all ages can suffer from this, especially those facing long-term stress or anxiety.
- Reversibility – Managing stress through relaxation techniques, therapy, and lifestyle changes can help you to promote eyebrow regrowth.
Scarring vs. Non-Scarring Eyebrow Hair Loss
Eyebrow hair loss can be categorized into two types: scarring madarosis and non-scarring madarosis. Understanding the difference between these types is crucial for determining the right treatment approach.
Differences Between Scarring and Non-Scarring Madarosis
- Scarring Madarosis: This type of hair loss happens when your hair follicles are permanently damaged due to skin conditions, trauma, or infections. The hair cannot regrow because the follicles are destroyed and replaced by scar tissue.
- Non-Scarring Madarosis: This type is temporary and occurs due to hormonal imbalances, stress, nutritional deficiencies, or medical conditions. Since the hair follicles remain intact, regrowth is possible with the right treatment.
Common Causes of Scarring Hair Loss
Scarring madarosis can result from various factors, including:
- Skin Conditions: Diseases like lichen planopilaris, discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE), and frontal fibrosing alopecia cause inflammation and scarring on the skin, leading to permanent hair loss.
- Burns or Trauma: Physical injuries, chemical burns, and radiation therapy can damage the hair follicles, making regrowth impossible.
- Infections: Severe bacterial, fungal, or viral infections like tinea capitis (ringworm of the scalp/eyebrows) or leprosy can cause scarring and permanent eyebrow hair loss if left untreated.
Eyebrow Hair Loss Causes
Main Reasons Behind Eyebrow Thinning
It can occur due to various medical, lifestyle, or environmental factors. Understanding the underlying causes of this condition is important in identifying potential treatments and prevention strategies. Below, we delve into some of the common causes that contribute to it
– Medical Causes of Eyebrow Hair Loss
Various medical conditions can lead to eyebrow loss, including thyroid disorders, autoimmune diseases, and certain skin diseases.
- Thyroid Disorders: Hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism can cause changes in hair growth, including thinning of the eyebrows. In such cases, hair loss is often one of the first visible symptoms.
- Autoimmune Conditions: Alopecia areata is a condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, leading to patchy hair loss in the eyebrows and other areas. Another autoimmune condition that may cause it is lupus.
- Skin Diseases: Conditions like eczema, psoriasis, or seborrheic dermatitis can inflame the skin around the eyebrows, leading to irritation and hair loss. Infections from these skin conditions further contribute to thinning or complete loss of eyebrow hair.
– Lifestyle Factors Leading to Eyebrow Hair Loss
Lifestyle choices and daily habits play a significant role in eyebrow health. Certain habits can result in or exacerbate it.
- Poor Diet: A nutrient-deficient diet that lacks essential vitamins and minerals such as biotin, zinc, and iron can lead to weakened hair follicles, making the eyebrows more prone to shedding. Malnutrition can stunt the hair growth process.
- Stress: Chronic emotional or psychological stress often leads to telogen effluvium, where hair prematurely enters a resting phase and falls out. During stressful times, people often notice an increase in eyebrow hair shedding.
- Lack of Proper Hair Care: Over-plucking, frequent waxing, or using harsh chemicals on the eyebrows may damage the follicles and contribute to eyebrow thinning or permanent hair loss.
– Infections or Physical Damage to the Eyebrows
Infections or external physical factors can also cause significant loss of eyebrows.
- Dermatitis: Both contact dermatitis and atopic dermatitis can affect the skin around the eyebrows. These skin conditions trigger inflammation and irritation, leading to hair loss in the area. Dermatitis can make hair follicles weak, impairing normal growth cycles.
- Traction Alopecia: This type of hair loss occurs when consistent pulling on the hair causes tension on the hair follicles. Common in individuals who frequently use eyebrow grooming tools (such as threading, tweezing, or tight makeup) that pull on eyebrow hairs, traction alopecia can weaken the hair roots over time, resulting in thinning or complete hair loss in extreme cases.
- Infections: Bacterial or fungal infections, particularly in the skin around the eyebrows, can damage hair follicles and lead to shedding or scarring.
Eyebrow Hair Loss Symptoms
Understanding about Symptoms of Eyebrow Loss
Identifying the symptoms of it is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. These symptoms can range from mild thinning to complete hair loss, depending on the underlying cause.
- Thinning and Sparsity of Eyebrows: This is one of the earliest signs. You may notice fewer hairs on your eyebrows, especially at the edges, where thinning commonly starts. The hair density may decrease uniformly, making the eyebrows appear lighter or less defined.
- Reduced Hair Volume: Eyebrows may begin to appear less full or uneven, particularly when hair follicles are weakened or inactive. This gradual loss may not be noticeable immediately but becomes evident over time when comparing older photographs.
- Patches of Missing Hair: Individuals may develop patchy areas where hair is entirely absent. These patches are often irregular in shape and can result from autoimmune conditions like alopecia areata or physical damage like traction alopecia.
- Complete Loss of Eyebrows: This is less common but can occur due to severe conditions, such as advanced thyroid disorders, chemotherapy, or scarring skin diseases. In such cases, the hair loss extends to the entire eyebrow, leaving little to no regrowth potential.
Eyebrow Hair Loss Prevention
How to Maintain Healthy and Fuller Eyebrows
Preventing eyebrow hair loss includes a combination of proper nutrition, healthy grooming habits, and stress management. Since both internal and external factors influence hair health, adopting a holistic approach can help maintain thick, healthy eyebrows while reducing the risk of excessive shedding.
– Key Preventative Measures
Maintaining strong and healthy eyebrows starts with proper nutrition, avoiding harmful grooming practices, and managing stress effectively.
- Balanced Diet – Nutrients like biotin, iron, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids play a crucial role in hair health. A diet rich in leafy greens, nuts, fish, eggs, and seeds can help strengthen hair follicles and prevent thinning.
- Avoid Over-Plucking and Harsh Treatments – Frequent tweezing, waxing, or threading can weaken hair follicles, leading to permanent eyebrow thinning over time. Harsh beauty products, including chemical-laden brow gels and dyes, can also contribute to your hair loss.
- Stress Management – Chronic stress increases cortisol levels, which can disrupt your hair growth cycle. Engaging in yoga, meditation, deep breathing, or other relaxation techniques helps regulate stress and supports healthy hair growth.
– Proper Eyebrow Care Routine
A daily eyebrow care routine can help nourish and protect the hair, reducing breakage and promoting healthier growth.
- Gentle Cleansing and Moisturizing – Using a mild, sulfate-free cleanser helps remove dirt and oil buildup without stripping moisture from your eyebrow. Applying a lightweight moisturizer or aloe vera gel keeps the skin around the eyebrows hydrated.
- Natural Nourishment with Castor Oil – Castor oil is rich in essential fatty acids and vitamin E, which strengthen hair follicles and encourage eyebrow growth. Applying a few drops to the eyebrows daily can promote thickness and reduce hair fall as well.
- Using Natural Remedies – Aloe vera, coconut oil, and vitamin E oil provide nourishment and prevent dryness, which can contribute to eyebrow thinning. Regular application helps condition the eyebrows, making them appear fuller over time.
Strong brows start with healthy skin. When the skin is well-hydrated and nourished, your eyebrows look naturally fuller and more defined.
Skin Confidence Awaits
Clear pores, smooth texture, and youthful radiance—HydraFacial is the self-care your skin has been waiting for
The Role of Hormones in Eyebrow Hair Loss
Understanding Hormonal Influence on Eyebrow Thinning
Hormones play a significant role in regulating hair growth and shedding throughout the body, including the eyebrows. Imbalances in hormonal levels can disrupt this delicate balance, leading to eyebrow thinning or complete hair loss.
- Thyroid: Both hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) can contribute to it. A common symptom of hypothyroidism is the loss of hair from the outer third of the eyebrows.
- Pregnancy and Postpartum Period: Fluctuating hormone levels during and after pregnancy can temporarily affect hair follicles. While most women experience scalp hair shedding postpartum, eyebrows can also become thinner.
- Menopause: Decreased estrogen levels during menopause often lead to thinning hair, including eyebrows, as estrogen supports hair follicle health and regeneration.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): PCOS causes elevated androgen levels in women, which may disrupt normal hair growth patterns, leading to eyebrow thinning or loss.
Hormones present in both men and women play a vital role in eyebrow hair growth and loss. Excess androgens, as seen in conditions like PCOS & PCOD, can weaken hair roots , while low androgen levels in aging individuals may cause thinning eyebrows.
When to See a Doctor
Signs You Should Consult a Doctor for Eyebrows
It may sometimes be a natural part of aging or linked to temporary factors, but in many cases, it can signal an underlying medical condition. Knowing when to seek professional advice can make a crucial difference in reversing the loss and addressing its root causes.
- Rapid Loss of Eyebrows: Sudden and noticeable shedding of eyebrow hairs can point to an autoimmune disease or hormonal imbalance.
- Patchiness: Patches of missing hair often suggest alopecia areata or infections, which may require medical intervention.
- Pain or Discomfort: Redness, itchiness, or swelling around the eyebrows may indicate skin conditions such as dermatitis or fungal infections that need professional treatment.
Diagnosis for Eyebrow Hair Loss
Tests and Exams to Identify Eyebrow Hair Loss
Doctors use several tools to identify the cause of eyebrow hair loss:
- Blood Tests: These can reveal thyroid imbalances, nutrient deficiencies, or hormonal abnormalities.
- Skin Biopsy: A small sample of skin is examined to check for diseases like alopecia areata or infections.
- Dermatological Consultation: A detailed assessment by a dermatologist helps identify conditions affecting the hair follicles or skin around the eyebrows.
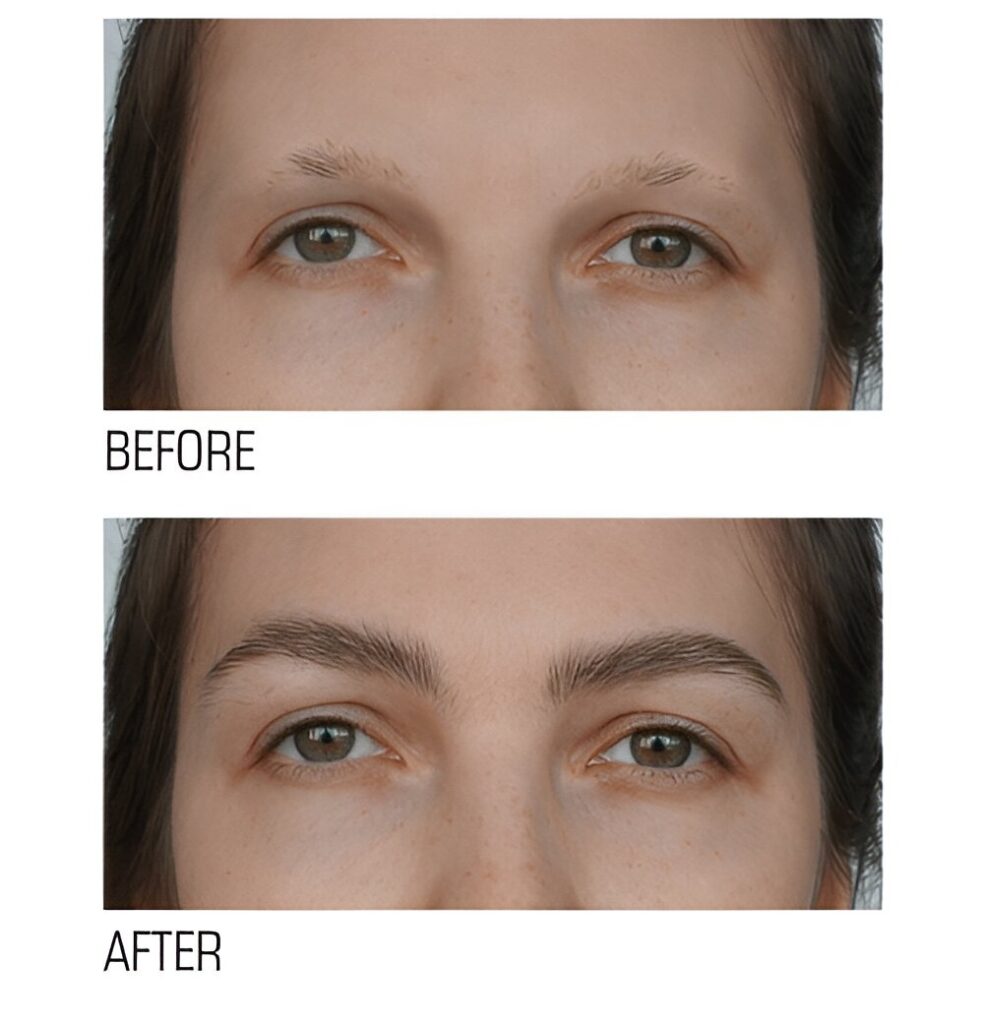
Eyebrow Hair Loss Treatment
Effective Treatment Options to Restore Eyebrow Hair Growth
When exploring eyebrow enhancement options, it’s important to understand the different treatments available, how they work, and who they are best suited for. Below is an overview of three popular methods: Microblading, Micropigmentation, and Eyebrow Tattooing Touch-Up Sessions (Semi-Permanent)
– Microblading for Thin Eyebrows
Microblading for Thin eyebrows is a semi-permanent makeup technique that uses a handheld tool with fine needles to create hair-like strokes, implanting pigment into the skin to mimic natural eyebrow hairs. This method is ideal for you seeking to enhance the fullness and shape of their eyebrows.
Who Is an Ideal Candidate for This Treatment
- People with sparse or thinning eyebrows.
- Those in good health without skin conditions near the brow area.
- Not suitable for those with oily skin, large pores, or deep wrinkles in the brow area, as these factors can affect pigment retention and healing.
Pregnant or nursing women should avoid this procedure.
– Micropigmentation for Eyebrows
Micropigmentation for eyebrows, often referred to as permanent makeup, involves using a machine to implant pigment into the dermal layer of the skin, resulting in a more solid and defined brow appearance. This technique is suitable for those desiring a more filled-in look.
Who Is an Ideal Candidate for This Treatment
- Not recommended for people with certain skin conditions or those who are pregnant.
- Best for those seeking a more defined and filled-in eyebrow appearance.
- Suitable for various skin types, including oily skin.
- Ideal for those without pigment allergies or a history of keloid scarring.
– Eyebrow Tattooing Touch-Up Sessions (Semi-Permanent Makeup)
Eyebrow Tattoo Touch up sessions are essential for maintaining the appearance and longevity of semi-permanent eyebrow treatments. These sessions help adjust the shape, color, and fullness of the brows as the pigment fades over time.
Who Is an Ideal Candidate for This Treatment
- Generally recommended every 12–18 months to maintain the best appearance.
- Not suitable for those experiencing significant skin changes or conditions in the brow area since the initial procedure.
- For people who have previously undergone microblading or micropigmentation.
- Ideal for those noticing fading or slight shape irregularities in existing eyebrow tattoos.
Conclusion
Eyebrow Hair Loss
Eyebrow hair loss, or madarosis, can have a profound impact on self-confidence and appearance. Identifying the root cause whether medical, lifestyle, or stress-related—is essential for effective treatment and prevention.
From medical interventions like topical treatments, oral medications, and eyebrow transplantation to lifestyle adjustments and safe grooming practices, there are numerous ways to address and manage it.
By understanding the importance of proper eyebrow care, maintaining a balanced diet, and seeking timely medical advice, individuals can preserve their eyebrow health and regain their natural appearance.
FAQs
Eyebrow Hair Loss
-
What is madarosis?
Madarosis is the loss or thinning of eyebrow or eyelash hair due to medical conditions, genetics, or lifestyle factors. It can be temporary or permanent, depending on the cause, and may require medical treatment for regrowth.
-
Can eyebrow hair loss be reversed?
In many cases, eyebrow hair loss is reversible if treated early. Medical treatments, dietary improvements, and proper care can promote regrowth. However, permanent hair loss, like scarring madarosis, may require solutions such as transplants.
-
What are the common causes of it?
Common causes include thyroid imbalances, autoimmune diseases, chronic stress, vitamin deficiencies, infections, and over-grooming practices like excessive plucking, waxing, or using harsh cosmetic products on the eyebrows.
-
Are there effective medical treatments for it?
Yes, treatments such as Minoxidil, corticosteroid injections, hormone therapy, and PRP therapy can help restore hair growth. For severe cases, procedures like eyebrow transplants or microblading offer long-term solutions
-
Can diet influence eyebrow health?
Yes, a diet rich in vitamins A, E, D, and minerals like zinc and iron supports healthy hair follicles. Protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and biotin also promote strong, thick eyebrows and prevent excessive hair thinning.
-
How can I prevent eyebrow hair loss?
Preventing eyebrow hair loss involves maintaining a balanced diet, using gentle grooming techniques, avoiding over-plucking or waxing, limiting chemical exposure, and managing stress through relaxation techniques like meditation or yoga.

