Skin tanning is something many of us deal with, especially if we spend time outdoors. In a country like India, where sunlight is strong for most of the year, it’s common for people to wonder what is the reason for skin tanning, particularly when they notice their skin getting darker despite regular care.
According to a 2023 skincare survey, over 65% of Indian women and 35% of men experience visible tanning, most commonly on the face, arms, and neck. Similar patterns are seen globally in regions with high UV exposure, such as Australia and the UAE, where nearly 1 in 3 individuals report sun-induced skin darkening.
Students, athletes, daily commuters, and outdoor workers are among the most affected. However, sun exposure is not the only answer to what is the reason for skin tanning. Factors like air pollution, hormonal changes and irregular skincare routines can also contribute to skin darkening and dullness.
While mild tanning may fade on its own, deeper or repeated tanning often needs proper care or treatment. Understanding the cause behind skin tanning helps in choosing the right prevention methods and treatments, instead of relying on guesswork.
In this blog, we break down skin tanning, the common causes behind it, and the right ways to manage and prevent it.
What is Skin Tanning?
Understanding Why Our Skin Gets Darker
Skin tanning is your body’s natural defense mechanism triggered by ultraviolet (UV) rays. When skin is exposed to sunlight, it reacts by producing more melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. This increased melanin rises to the surface, giving your skin a darker appearance, which we recognize as tanning.
Tanning primarily occurs due to the influence of UVA and UVB rays. UVB rays impact the top layer of the skin, leading to sunburn and delayed tanning, while UVA rays penetrate deeper, causing immediate tanning and long-term skin damage. Though often considered temporary, frequent exposure can cause lingering discoloration and dullness.
It’s important to distinguish tanning from other types of pigmentation. Tanning typically fades with time and care, whereas pigmentation due to hormonal or inflammatory causes tends to persist longer and may need treatment.
Tanning is not just a cosmetic change it’s a biological sign that your skin is trying to protect itself. Ignoring it may lead to premature aging or uneven skin tone over time.
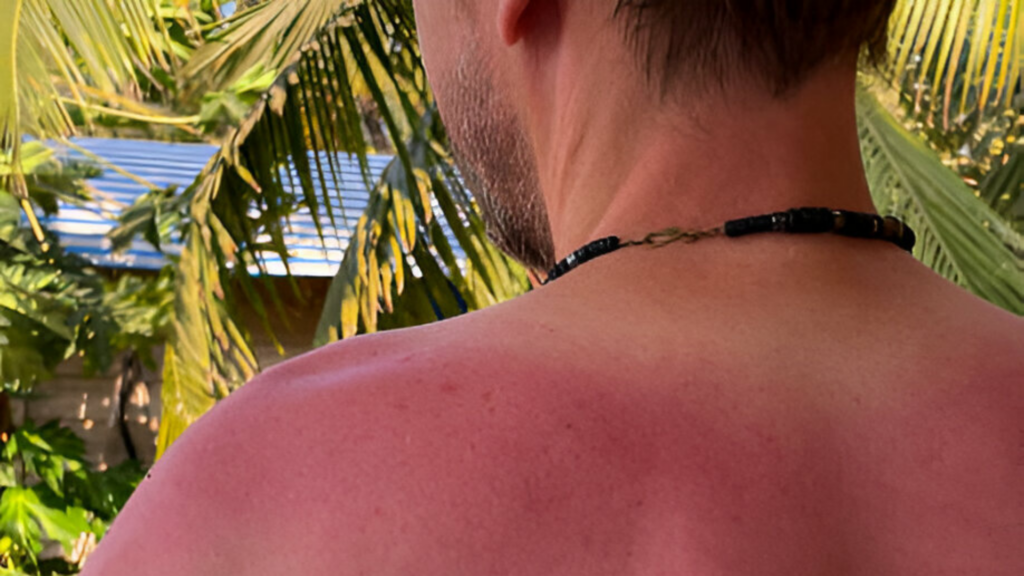

Types of Tanning
Types of Skin Tanning You Should Know
Tanning doesn’t look the same on everyone. The depth, shade, and pattern of tanning can vary based on factors like skin type, sun exposure duration, and even lifestyle. Here are the most common types of tanning seen in both Indian and global populations:
– Sun Induced Tanning
This is the most common type and happens due to prolonged exposure to natural sunlight, especially UVB and UVA rays. It often affects the face, arms, neck, and feet—areas usually left uncovered.
– Tanning from Artificial Sources
Tanning beds and sunlamps, popular in some Western countries, emit UV rays similar to the sun. This type of tanning may be more even but carries the same risks as natural tanning, including early skin aging and increased chances of skin damage.
– Patchy Tanning
Often seen in those with uneven sun exposure or inconsistent sunscreen use. It results in blotchy or patchy skin tones and is a common concern among those who drive frequently or wear sleeveless clothing.
– Occupational Tanning
Seen in people who work outdoors such as farmers, construction workers, and delivery staff. This type of tan tends to be long-term and deeper due to repeated daily exposure.
– Hormonal or Blue Light-Induced Tanning
Even without stepping into the sun, hormonal changes (like during PCOD, pregnancy, menopause) or long exposure to blue light from mobile and laptop screens can cause tanning or dullness especially on the face.
Early and Common Signs of Skin Tanning
Visible Signs That Show You’re Tanned
Skin tanning doesn’t always appear the same way. In some people it shows up as mild dullness, while in others it leads to patchy darkening, sensitivity, or visible tan lines. These changes often depend on how deep the tanning is and what’s causing it.
- Rough or dry texture
- Dull and tired appearance
- Uneven skin tone
- Increased skin sensitivity
- Difficulty in applying makeup smoothly
- Skin feels warm or tight
- Faded tan lines
What is the Reason for Skin Tanning?
What Causes of Skin Tan
Skin tanning happens due to a mix of natural skin responses and external factors. When the skin is exposed to certain triggers, it produces more pigment to protect itself, which leads to darkening over time. Understanding these causes makes it easier to manage and prevent unwanted tanning.
– UV Rays Exposure (UVA & UVB)
The most common cause of skin tanning is exposure to the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays.
- UVA rays penetrate deep into the skin and cause immediate darkening
- UVB rays affect the outer layer of the skin and lead to delayed tanning or sunburn
Both types of rays trigger melanin production, which is the skin’s natural defence against damage. Repeated or unprotected exposure often results in long-lasting tan lines, uneven tone, or skin sensitivity.
– Melanin Response & Skin Type
Melanin is the pigment that gives skin its colour and plays a key role in tanning.
When UV rays hit the skin, melanin production increases. People with lighter skin may burn more easily, while those with darker skin tones often tan faster or deeper. This difference in response is largely genetic and explains why some people tan quickly even with limited sun exposure..
– Environmental, Hormonal & Lifestyle Triggers
Not all tanning comes directly from sunlight.
- Air pollution and hot climates can increase skin sensitivity
- Reflective surfaces like water, roads, and concrete intensify UV exposure
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy, PCOD, menopause, or contraceptive use can make skin more reactive
Certain medications and cosmetic products may also increase photosensitivity. This is why many people notice facial tanning even when they don’t spend much time outdoors. Long screen hours and blue light exposure may also contribute to gradual skin dullness.
In short, skin tanning is not caused by the sun alone. Your skin type, environment, hormones, and daily habits all influence how and why tanning develops.
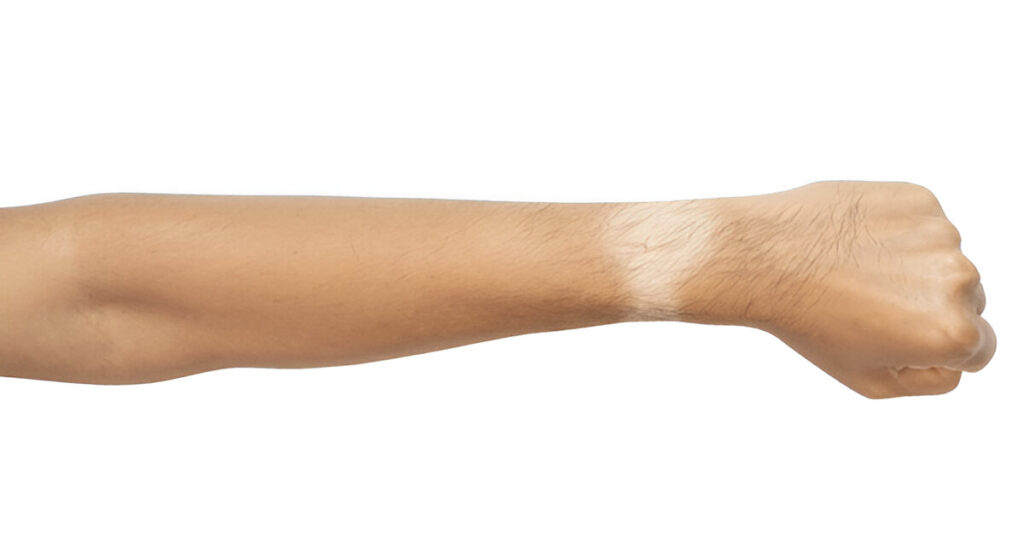
How Tanning Is Different from Pigmentation
Tanning vs Pigmentation
Tanning and pigmentation are both related to skin color changes, but they are not the same. Many people confuse the two, as both conditions involve darkening of the skin.
However, the causes, appearance, and duration of tanning and pigmentation are quite different.
Key Differences Between Tanning and Pigmentation:
| Aspect | Tanning | Pigmentation |
| Cause | Caused by sun exposure (UV rays) | Triggered by hormonal changes, acne, injury, medication, or medical conditions |
| Appearance | Uniform darkening on exposed areas (face, arms, neck) | Appears as patches, spots, or uneven discoloration |
| Duration | Fades naturally over time with skincare, sun protection or treatment | Takes longer to fade, often needs treatment like creams or laser therapy |
| Location | Found mostly on sun-exposed body parts | Can appear anywhere, including non-exposed areas |
| Prevention | Preventable with sunscreen, protective clothing, avoiding peak sun hours | Requires managing internal factors and using targeted skincare |
Is Tanning Always Bad?
Can Tanning Ever Be Good for You?
Tanning is often perceived as a sign of a healthy glow, but its effects on skin health can be mixed. In moderation, sun exposure helps the body produce vitamin D, essential for bone health and immunity.
However, excessive or repeated tanning especially without sun protection can lead to long-term damage.
Unprotected exposure to UVA and UVB rays speeds up skin aging, causes sunburns, and increases the risk of pigmentation and even skin cancer.
Artificial tanning methods like tanning beds also carry similar risks. People with lighter skin tones or a history of skin sensitivity may experience faster and more severe effects.
While occasional tanning might not be harmful if managed carefully, intentional and prolonged exposure without protection is considered risky. Dermatologists recommend using sunscreen daily, limiting direct sunlight during peak hours, and choosing safer alternatives like sunless tanning lotions if desired.
How to Remove Tan Naturally
How to Remove Tan at Home
If you’re dealing with mild to moderate tanning, some good old home remedies might help you! Ingredients like aloe vera, lemon juice, tomato pulp, curd, and turmeric are popular for a reason they’re gentle on skin and help brighten it naturally.
Want to focus on specific areas? you can check our detailed guides on How to Remove Tan from Face and How to Remove Tan from Body for step-by-step tips.
Treatments for Tanning
Skincare Treatments That Fade Tanning
If persistent tanning is affecting your skin’s tone and texture, advanced dermatological treatments can offer visible results. Two commonly recommended procedures are Q-Switch Laser and Chemical Peels, especially effective for deeper tanning and dullness caused by sun exposure.
– Q-Switch Laser for Tan
Q-Switch Laser for tan is a precise treatment that targets excess melanin in the skin without damaging surrounding tissues. The laser energy breaks down melanin pigments, which are naturally flushed out by the body over time. It’s highly effective for treating stubborn tanning on areas like the face, neck, and arms. Multiple sessions may be needed based on the depth of the pigmentation.
– Chemical Peel for Tan and Dullness
Chemical peels for tan & dullness involve the controlled exfoliation of your top skin layers using fruit acids or medical-grade solutions like glycolic or lactic acid. These peels help remove dead skin cells, improve cell turnover, and reduce the appearance of tanning and surface dullness.
They’re suitable for both dry and oily skin types and can restore a more radiant, even complexion.
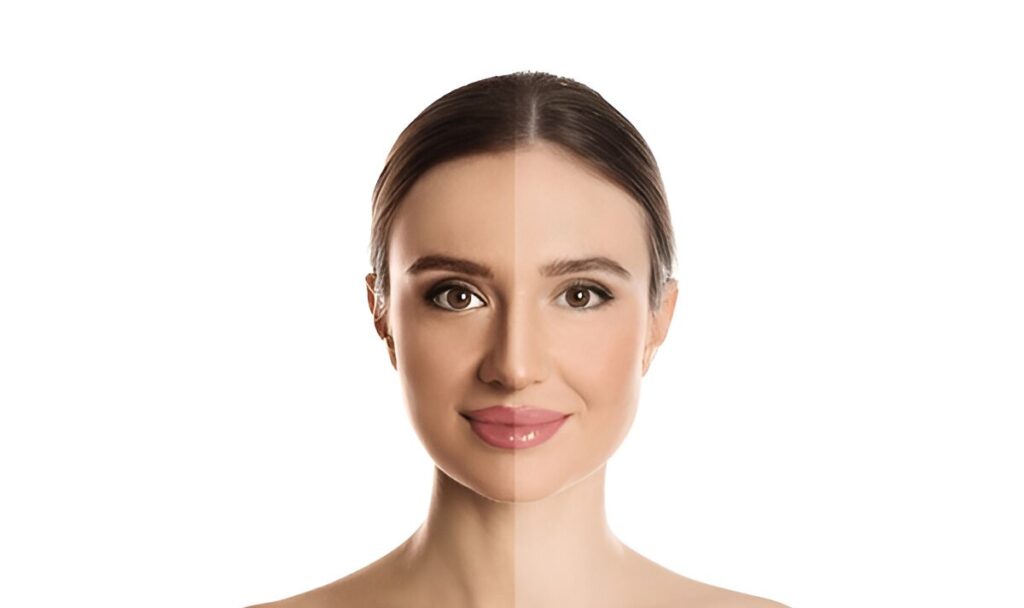

Prevention of Tanning
Prevention Tips For Avoiding Tanning
Preventing skin tanning requires a combination of mindful skincare habits, a balanced diet, and protective clothing. These strategies help shield your skin and reduce long-term sun damage.
– Sunscreen & Sun-Protective Habits
A consistent sunscreen routine paired with conscious sun exposure decisions can drastically reduce the risk of tanning and protect your skin from deep UV-induced damage.
- Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30 or more) 15–20 minutes before stepping out.
- Reapply every 2–3 hours, especially during swimming or sweating.
- Use mineral sunscreens with zinc oxide or titanium dioxide for better UVA/UVB coverage.
- Avoid direct sun exposure between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
- Use lip balms with SPF and avoid tanning beds entirely.
– Diet & Hydration Tips for Defense
Your internal health reflects on your skin. A nutrient-rich diet boosts your skin’s natural defense mechanisms and helps in faster recovery from minor sun damage.
- Consume vitamin C-rich fruits (oranges, kiwi) and leafy greens.
- Include vitamin E sources like almonds and sunflower seeds.
- Drink at least 8–10 glasses of water daily to keep skin hydrated.
- Add foods with beta-carotene (carrots, pumpkin) to support skin health.
- Omega-3-rich foods like walnuts and flaxseeds can improve skin resistance to UV rays.
– Clothing & Shade Strategies
Your outfit choices can serve as an effective shield. Wearing the right fabrics and accessories helps in reducing direct sun contact, especially in hot and sunny climates.
- Choose full-sleeved, lightweight cotton or linen clothing.
- Wear wide-brimmed hats and UV-block sunglasses.
- Use umbrellas or scarves while walking under the sun.
- Opt for darker or tightly woven fabrics, which offer better UV protection.
- Sit or walk in shaded areas whenever possible.
Protect Your Skin Every Day with RSB Sunscreen SPF 50
Keep tanning, sunburn, and dullness away with broad-spectrum protection. Lightweight, non-greasy, and perfect for Indian weather.
Conclusion
What is the Reason for Skin Tanning?
Skin tanning is a common problem in India due to our strong sun and daily exposure. Regular or deep tanning can damage the skin in the long run. It’s not just the sun pollution, hormonal issues, and stress also play a role in making our skin look dull and darker.
The good thing is tanning can be reduced. For light tanning, home remedies like aloe vera, tomato pulp, or curd can help. If your skin is deeply tanned, treatments like chemical peels or Q-switch lasers give better results.
Prevention is always better than cure protecting your skin daily is easier than reversing damage later.
So, never skip your sunscreen, drink plenty of water, eat healthy fruits and veggies, and cover your skin properly while going out. These small habits can save your skin from long-term damage.
Always remember, glowing skin is not about being fair it’s about keeping it healthy and cared.
Frequently Asked Questions
Common Questions About Skin Tanning
-
What is skin tanning?
Tanning is the process where your skin becomes, This happens when UV rays trigger melanin production, the pigment that gives skin its color, as a natural way to protect deeper skin layers.
-
Is tanning permanent or temporary?
Tanning is usually temporary and fades over time with proper care. However, if the tanning is deep or repeated frequently, it may take longer to fade and might need treatment to restore the skin tone.
-
Does sunscreen prevent tanning completely?
Sunscreen helps reduce tanning by blocking UV rays, but it doesn’t completely stop it. Regular use of SPF 30+ sunscreen and reapplication every few hours gives better protection against both tanning and sun damage.
-
How long does it take to remove tan?
Tan removal time depends on depth. Mild tanning can fade in 1–2 weeks with skincare, while deeper tanning may take 3–4 weeks or need treatments like chemical peels or laser for faster and better results.
-
Are home remedies useful in removing tan?
Yes, home remedies like aloe vera, curd, lemon, and turmeric help reduce mild tanning naturally. They brighten the skin and improve tone with regular use, but may not work well on deeper or old tanning.
-
Which treatments are best for tan removal?
Q-switch laser and chemical peels are the most effective treatments. They target excess melanin, remove dead skin, and brighten dull areas. These are safe when done by professionals and give long-term visible results.
-
Can tanning affect both men and women?
Yes, tanning affects both men and women equally. Any exposed skin, like the face, neck, arms, or hands, can develop tan with repeated sun exposure, regardless of gender or age group.
-
What is the Reason for Skin Tanning?
Skin tanning happens mainly due to exposure to UV rays from the sun, which increases melanin production in the skin. Other causes include pollution, hormonal changes, stress, and certain medications that make skin more sensitive to sunlight.
Author
-

Radhika Gupta is the CEO and guiding force behind RSB Wellness, where she blends science-backed knowledge with a deep commitment to holistic well-being. With a clear focus on integrative care, she leads the mission to empower individuals to take control of their health through personalized, practical strategies. Passionate about education and results-driven wellness, she brings both expertise and empathy to every article and initiative.

